On December 10, 2020, the European Union issued a draft proposal for a new battery law. It intends to abolish the current EU battery directive (2006/66/EC) to ensure the sustainability, high performance and performance of batteries placed on the EU market throughout the life cycle. safety.
The new battery regulations require risk assessment and risk management of the substances used in batteries, update the restrictions and exemptions for related hazardous substances, and require the committee to pass authorization when it finds that the substances used or present in batteries are harmful to humans or the environment The bill adds restricted substances. The draft of the new battery law also updates the label specification, requiring the addition of a description of hazardous substances and safety risks in the label.
1. Requirements for the control of toxic and hazardous substances
The new battery regulations still maintain the current EU battery directives on mercury and cadmium in batteries, but the restrictions and exemptions have been updated, and new restrictions on toxic and hazardous substances have been introduced, as follows:
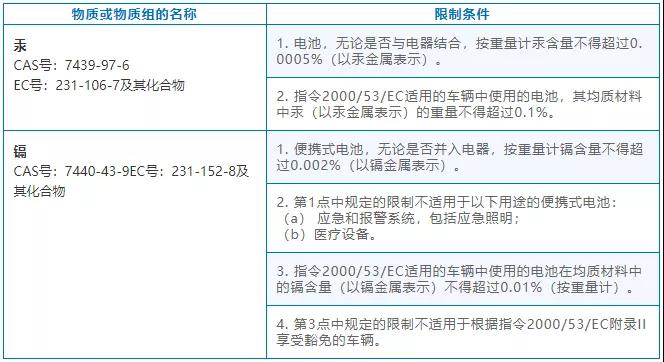
2. Label and information requirements
The new battery regulations update the labeling and information requirements, stipulating that from January 1, 2027, a label containing basic battery information should be attached to the battery, including manufacturer information, battery type, chemical composition, removal of lead, cadmium, and mercury Eight items including other hazardous substances and key raw materials. All batteries need to be marked with a separate collection mark (crossed wheeled trash can mark). When the cadmium content is greater than 0.002%, or the lead content is greater than 0.004%, the symbol corresponding to the excess element must be marked under the trash can. Also need to mark the battery capacity.
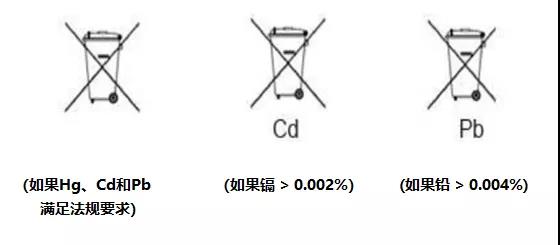
3. Requirements for battery waste management
In the treatment of used batteries, landfill, incineration, composting, and imperfect reuse methods may all cause secondary pollution and harm the environment. In Switzerland, there is a factory specializing in the treatment of waste batteries that uses the "heat treatment" method to grind the old batteries and heat them in the furnace; related German companies use "wet treatment" to extract various metals from the electrolyte solution with the help of ionic resins. And "vacuum heat treatment method" to dispose of used batteries. In contrast, the domestic treatment methods for waste batteries are not yet complete, and it is necessary to further develop mature waste battery treatment technologies.
Specifically, in dealing with environmental pollution of used power batteries, current electric vehicle companies generally adopt two methods: recycling and extending battery life. Tesla recycled 1,430 tons of waste battery metal globally in 2019, achieving 100% recycling. The battery pack life is designed to exceed the service life of the vehicle. When the vehicle runs 150,000 to 200,000 kilometers, the average degradation of the battery is less than 15%. Therefore, from the perspective of business and environmental protection, the future improvement of battery life and cruising range is the common goal of car companies and users. Achieving these two points can also reduce environmental pollution caused by waste batteries.
Reminder
When producing batteries, battery suppliers should limit the use of hazardous substances in batteries to meet the requirements for products placed on the EU market. At the same time, the focus is on reducing the existence of such substances in waste, which can be solved by properly collecting and recycling portable batteries. In the new battery regulations, there are also separate revision requirements for the battery collection rate. In addition, it is recommended that relevant companies establish a waste management mechanism and improve the management level to ensure that the secondary raw material market operates well, while preventing and reducing the battery production and use process, as well as the disposal at the end of the battery life, including recycling and other environmental impacts .













